How to Proactively Manage Risk for Advanced Medical Device Manufacturers
Advanced medical devices are revolutionizing patient outcomes by providing innovative solutions to challenging conditions. Even so, regulatory agencies and advanced medical device companies are fully aware that devices can pose significant patient risks in the product life cycle from faulty design, development, or manufacturing.
Regulatory agencies and advanced medical device companies are fully aware that devices can pose significant patient risks in the product life cycle from faulty design, development, or manufacturing. Share on XProactively managing risk is crucial for advanced medical device manufacturers to ensure patient safety and product success. Let’s take a look at how advanced medical device manufacturers can proactively manage risk throughout the product lifecycle.
What is Risk Management for Advanced Medical Devices?
Risk management for advanced medical devices is identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and controlling potential risks associated with the device’s development, manufacturing, distribution, and use. Mitigating risk involves a systematic approach to identifying potential hazards, assessing the relative risks, and implementing controls to minimize or eliminate risks.
Effective risk management is essential for advanced medical device manufacturers to ensure their products meet the required safety and regulatory standards. An advanced medical device Risk Management Plan should include the following criteria:
- Scope – the definition of the product or products.
- Intended use of the product(s).
- List of all planned risk management activities throughout the product life cycle.
- Roles and responsibilities of the risk management team.
- Relevant criteria for the product’s risk profile.
- Methodology to verify risk control measures.
- Specify how post-production feedback loops will integrate into risk management activities for the product.
The Risk Management Plan isn’t a static document, it will evolve and should be kept current, even after product development is completed.
Advanced Medical Device Risk Management Standard – ISO 14971
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published ISO 14971, the standard for risk management in medical devices. ISO 14971 provides a comprehensive framework for managing risks associated with medical devices throughout the product lifecycle.
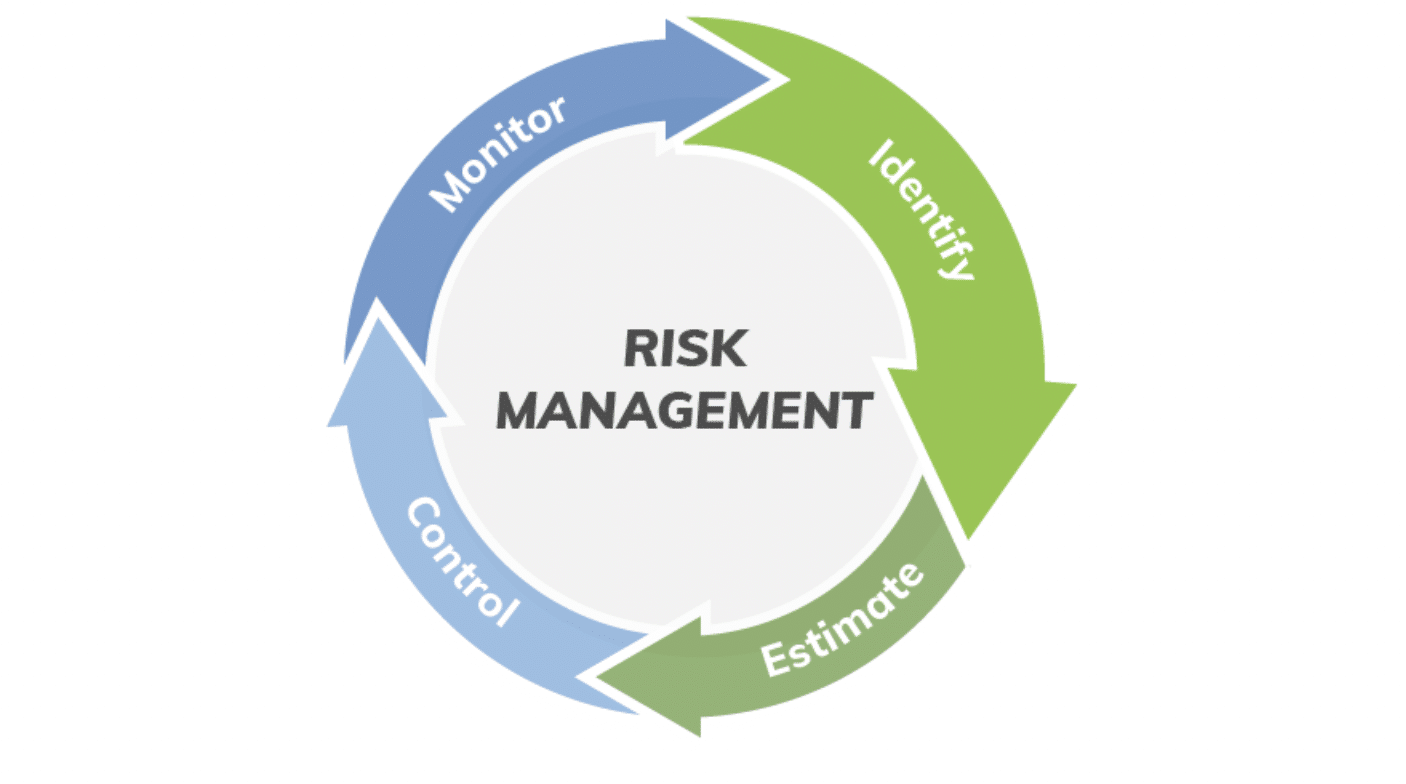
A good way to think about a complex process is to step back to the 20,000-foot view. The ISO is a helpful document for organizing risk management as an overall four-part process that includes:
- Identify the hazards associated with a medical device.
- Estimate and evaluate the associated risks.
- Control these risks.
- Monitor the effectiveness of these controls.
In addition to ISO 14971, several other key medical device industry standards require risk management, including:
- IEC 60601 – a series of technical standards for the safety and essential performance of medical electrical equipment, published by the International Electrotechnical Commission.
- IEC 62366 – a standard with the goal of reducing errors caused by inadequate medical device usability.
- ISO 10993 – a series of standards for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices to manage biological risk
- ISO 13485 – a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices.
All the above standards refer to risk management and ISO 14971 as well.
Words matter: How ISO 14971 defines risk
By its nature, risk management relates to minimizing liability and litigation risk. It’s important that all parties are on the same page and are careful with terms and wording. Advanced medical devices should understand the ISO’s definitions for several key terms and be specific and consistent in the documentation. Below are several key terms and definitions:
- HAZARD: A potential source of harm.
- HAZARDOUS SITUATION: Any circumstance that exposes people, property, or the environment to one or more hazards.
- HARM: Physical injury, damage to health, property, or the environment caused by a hazard.
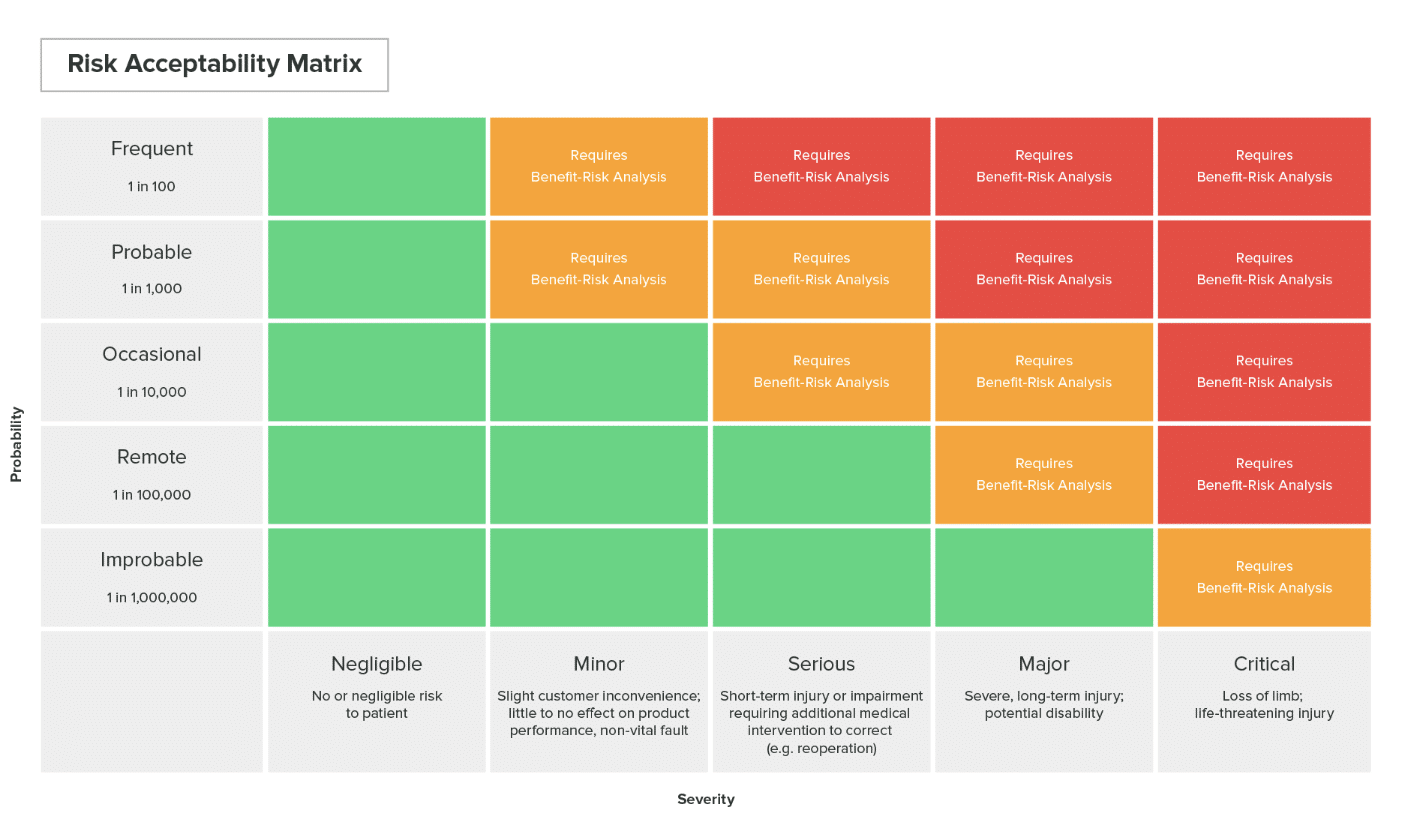
- SEVERITY: A measure of the potential consequences of a hazard.
- RISK: the combination of the probability of harm occurring and the severity of that harm.
- RISK MANAGEMENT: a systematic application of management policies, procedures, and practices to analyze, evaluate, control, and monitor risk.
- RISK ANALYSIS: a systematic use of available information to identify hazards and estimate the risk associated with them.
- RISK ESTIMATION: the process of assigning probabilities to harm occurrence and the severity of that harm.
- RISK EVALUATION: Comparing the estimated risk against given risk criteria to determine its acceptability.
- RISK ASSESSMENT: The overall process comprises a risk analysis and a risk evaluation.
- RISK CONTROL: The process of making decisions and implementing measures to reduce or maintain risks within specified levels.
- RESIDUAL RISK: The risk that remains after risk control measures have been taken.
Design Controls and Risk Management for advanced medical devices
An important connection for advanced medical devices to understand is the relationship between risk management and design controls. While design controls and risk management are closely related in the development process, resources are limited. Risk never goes to zero, so risk triaging is critically important.
During risk management, teams triage risk factors by systematically identifying, analyzing, and controlling potential risks associated with a medical device throughout its lifecycle.
Design controls are the set of procedures and practices that ensure the quality and safety of a medical device throughout its development and manufacturing process. Teams create design controls to ensure the device is designed and developed according to the intended use and meets the required safety and regulatory standards.
Design controls can help identify potential risks associated with the device’s design, materials, and manufacturing processes and ensure that risk control measures are in place to minimize or eliminate those risks.
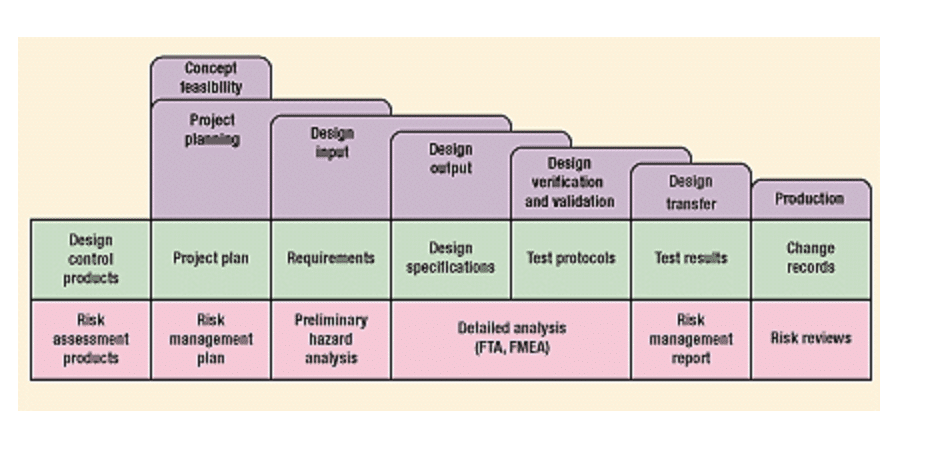
By integrating design controls and risk management, advanced medical device manufacturers can ensure that they are developing products safely and meet the required safety and regulatory standards. This chart shows the relationship between risk management and design controls:
Design controls and risk management work together to help manufacturers to reduce the risk of product recalls, litigation, and reputational damage associated with faulty medical devices.
Advanced Medical Device Risk Management Over Design and Product Life Cycle
Risk management is a part of the entire design and product lifecycle. Proactively managing risks associated with advanced medical devices covers three broad phases:
- Incorporating risk management into the design and development process
- Identifying potential risks related to manufacturing
- Continuously monitoring and evaluating risks throughout the product lifecycle
Design and Development
During the design and development phase, manufacturers should identify potential hazards associated with the device’s design, materials, and manufacturing processes and develop risk control measures to minimize or eliminate potential risks.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers should identify potential risks associated with manufacturing, including quality control, supplier quality, and product testing. Knowing the potential dangers helps them implement risk control measures to ensure that the final product meets the required safety and regulatory standards.
Product Lifecycle
Manufacturers should plan for feedback loops to continuously monitor and evaluate potential risks associated with the device throughout its lifecycle, including post-market surveillance, product updates, and modifications. Advanced medical devices should revisit and update post-market risk management strategies to mitigate risks from changing market conditions and scale customer experience with advanced medical device.
Moving Ahead
Proactively managing risks associated with advanced medical devices is crucial for ensuring patient safety and product success. Compliance with ISO 14971 and related standards is essential for advanced medical device manufacturers to ensure that their products meet the required safety and regulatory standards.
Risk management planning should be a part of your roadmap from day one. Do you have questions about specifics for your device? At Galen, we have extensive experience helping clients with this critical area. Reach out today to get the conversation started.