Securing the CE Mark in the EU Advanced Medical Device Market
The European medical device market presents a significant opportunity for innovative companies. With a growing population, half of which is over age 40, the increasing demand for advanced medical technologies in the EU offers a lucrative space for groundbreaking solutions.
However, navigating the regulatory landscape and securing the CE mark in the EU can be complex and pose significant challenges for companies unfamiliar with the specific requirements.
We’ll guide you through the changing environment and demystify the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and its implications for obtaining the coveted CE Mark.
Understanding the Changing Landscape of the EU Medical Device Market
The European device market is witnessing a surge in exciting new technologies. The rise of AI-powered devices, personalized medicine solutions, and connected healthcare systems is fueling significant market growth.
This trend towards more sophisticated and data-driven devices creates immense opportunities for companies at the forefront of innovation. However, for US companies accustomed to the American FDA regulatory framework, entering the EU market requires a strategic shift.
The EU has a set of regulations that ensure that legal manufacturers of medical devices adhere to their standards.
Before May 2021, these regulations were called Medical Device Directives (MDD). The European Union Medical Devices Regulations (EU MDR) replaced the MDD in May 2021. In this post, we refer to current regulations outlined by the EU MDR.
Demystifying the EU MDR and CE Mark
The EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), implemented in 2017, represents a significant shift in the regulatory landscape for devices within the European Union. The MDR aims to strengthen patient safety and transparency by establishing stricter device development, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance requirements.
Understanding the transition from the previous Medical Device Directives (MDD) to the MDR is vital. The MDR introduces a more rigorous approach to device classification, potentially requiring reclassification for some devices previously cleared under the MDD. This has implications for the level of scrutiny your device will undergo during the CE Mark certification process.
What is a CE Mark?
The CE Mark is an essential requirement for access to the EU market. The medical device CE symbol is a physical mark, often that looks like a sticker, that signifies that your device complies with EU safety and performance standards.
Navigating Classification and Compliance with the MDR
The MDR introduces a revised device classification system, potentially impacting your CE Mark journey. This system categorizes devices based on their intended purpose and potential risks, ranging from Class I (lowest risk) to Class III (highest risk). A key challenge lies in navigating this revised classification scheme.
Only medical devices meant for commercialization in the EU require CE marking. For example, a custom-made or clinical testing device does not require CE marking. Devices that don’t need a CE mark must comply with other regulations, so do your research before introducing a new medical device.
Some devices with low risk (non-sterile and non-measuring) can self-certify using the procedure outlined in the MDR. Medical devices that pose a perceived risk to the user must obtain a CE mark certification from a Notified Body.
In addition, devices with previous MDD clearance may face reclassification under the MDR, requiring them to meet stricter requirements.
Furthermore, the MDR raises the bar for technical files, documentation, and clinical evaluation reports (CERs). These documents are crucial in demonstrating your device’s safety and efficacy. The new regulations demand more comprehensive documentation outlining your device’s design, manufacturing, and risk management processes.
CERs also must now incorporate a broader range of clinical data to support your device’s safety and performance claims.
Risk Classification for CE Mark
The process of securing a CE mark depends on the class of the medical device you are trying to bring to market and determines what process you’ll need to go through to secure a CE mark.
Generally, the classification of a device depends on the level of risk associated with it:
Class I: Low risk
Class IIa: Low-medium risk
Class IIb: Medium-high risk
Class III: High risk
Many factors determine the perceived risk level, including whether a device is sterile, has a measuring function, or is highly invasive. If your medical device has in-vitro functionality, expect additional requirements.
For all other devices, the manufacturer must satisfy the “conformity assessment procedure” for the class of their medical device.
Mastering Post-Market Surveillance and Transparency
In addition to pre-market requirements, the MDR strongly emphasizes post-market surveillance (PMS) and vigilance, requiring manufacturers to actively monitor their devices’ performance once they are placed on the market.
This includes gathering and analyzing real-world data to identify potential safety concerns and implementing corrective actions if necessary. The MDR also strengthens vigilance requirements, mandating a proactive approach to identifying and reporting potential device-related incidents.
Enhanced traceability and transparency are also central to the MDR. The European Union Database on Medical Devices (EUDAMED) is a central repository for information on all devices marketed in the EU. The Unique Device Identification (UDI) system also assigns a unique identifier to each unit, facilitating easier tracking and identification for manufacturers and healthcare providers.
Maintaining detailed and up-to-date technical and safety documentation remains crucial under the MDR. This documentation must be readily accessible to support ongoing compliance efforts, including responding to potential safety concerns and collaborating with regulatory authorities.
Practical Steps for Securing CE Mark and Overcoming Challenges
Obtaining the coveted CE Mark signifies a significant milestone in your journey to market your device in the EU. While the process can be complex, understanding the critical steps can help you navigate it more efficiently.
The graphic below illustrates an overview of the steps to get a CE marking.
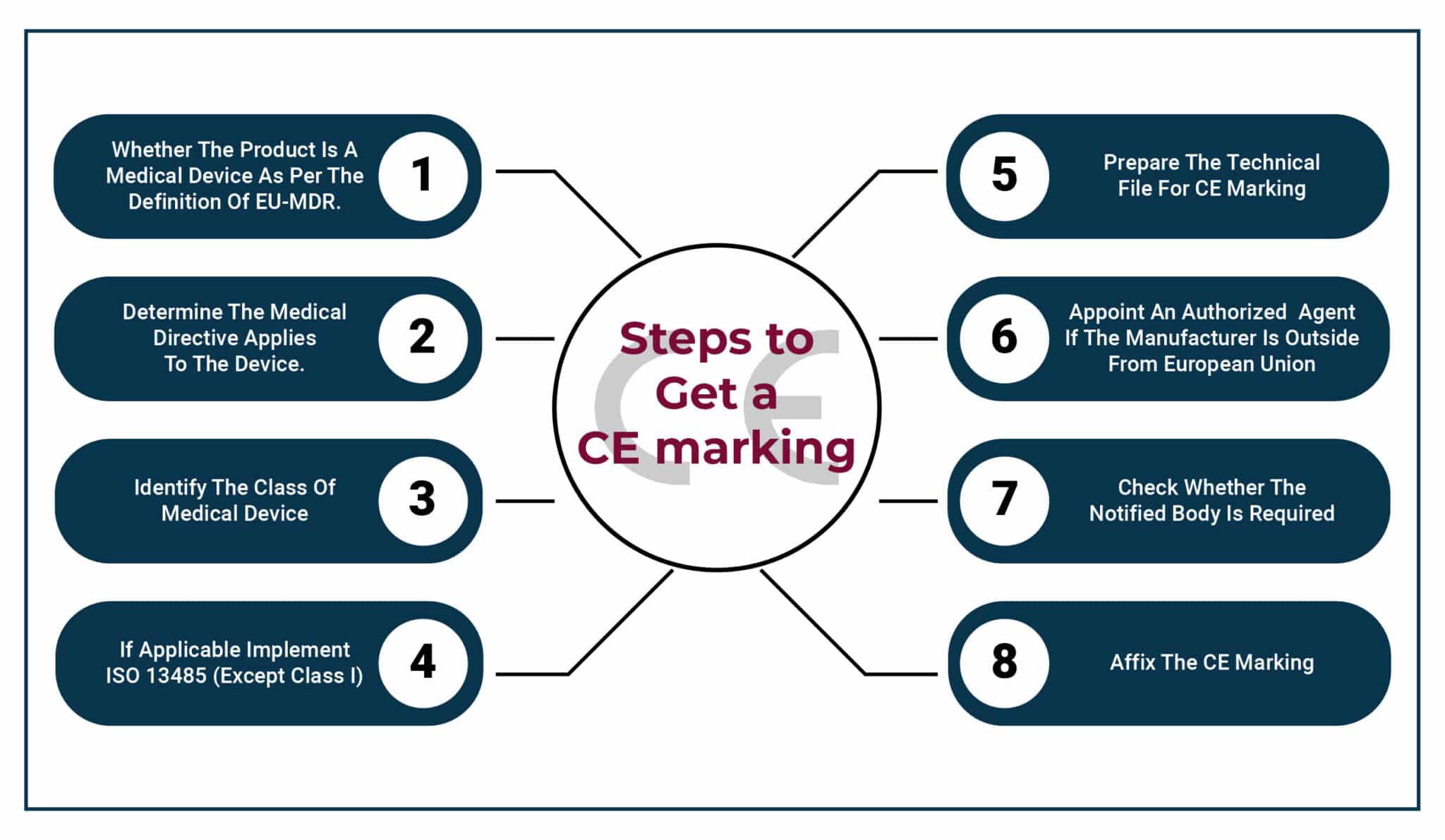
Source: SGS Munich Competence Center
CE Mark Certification Process: The European CE Mark certification process under the MDR can be broken down into the following key steps for devices that require CE marking.
Classification: As discussed earlier, accurately classifying your device under the CE certification/MDR is crucial. Consulting with a notified body can provide valuable guidance on proper classification.
Technical Documentation Preparation: Compile comprehensive technical files and documentation outlining your device’s design, manufacturing processes, and risk management strategies. Galen Data’s platform can simplify this step by providing a secure and organized environment for managing all your relevant technical data.
Clinical Evaluation: Conduct a thorough clinical evaluation to assess your device’s product compliance, safety, and efficacy. This may involve gathering data from clinical trials or existing literature. Galen Data can assist with data management for clinical evaluation activities.
Conformity Assessment Procedure: Based on your device’s classification, select the appropriate conformity assessment procedure. Once again, this may involve working with a notified body to assess your documentation and conduct audits.
CE Marking and Declaration of Conformity: Once you meet all requirements, you can affix the CE Mark to your device and issue a Declaration of Conformity attesting to its compliance with the MDR.
Labeling and Reprocessing Rules: The MDR introduces new requirements for CE-marked device labeling, including ensuring clear and concise instructions for use. Additionally, regulations surrounding single-use device reprocessing have been revised.
Collaboration and Adaptation: Successfully navigating the revised CE certificate process requires effective collaboration with notified bodies and other stakeholders. Staying informed about ongoing regulatory updates and adapting your approach is crucial for a smooth market launch.
Frequently Asked Questions about Securing the CE Mark in the EU
1. What is the CE Mark, and why is it important?
The CE Mark is a mandatory symbol signifying that your medical device complies with EU safety and performance standards. It’s essential for gaining market access within the European Union.
2. How has the EU MDR impacted obtaining the CE Mark?
The EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation) implemented stricter device development, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance requirements. This may involve device reclassification and more comprehensive technical documentation for CE Mark certification.
3. What are the key challenges of securing the CE Mark in the EU under the MDR?
Challenges include navigating the revised device classification system, preparing more rigorous technical documentation and CERs, and complying with enhanced post-market surveillance and vigilance requirements.
4. What are the main differences between the MDR and the previous MDD (Medical Device Directives)?
The MDR introduces a more rigorous approach to classification, potentially requiring reclassification for some devices. It also raises the bar for technical documentation and clinical evaluation reports.
5. What are the steps involved in obtaining CE Mark certification under the MDR?
Key steps include accurate device classification, compiling technical documentation, conducting a clinical evaluation, selecting a conformity assessment procedure, and affixing the CE Mark with a Declaration of Conformity.
6. How does the MDR emphasize post-market surveillance and transparency?
The MDR requires manufacturers to monitor device performance through real-world data collection and implement corrective actions if necessary. Additionally, it promotes transparency with the EUDAMED database and Unique Device Identification (UDI) system.
7. How can Galen Data assist companies in securing the CE Mark?
Galen Data’s secure cloud platform facilitates efficient data management for technical documentation, CER creation, and post-market surveillance activities, aiding compliance efforts. Our team has experience with…..
Moving Ahead
For advanced medical device companies, entering the EU market can be a lucrative yet complex process. Galen Data’s secure cloud platform can be a valuable asset in navigating these challenges. Our platform facilitates efficient data management, allowing you to securely collect, organize, and access critical data for comprehensive documentation and CER creation.
Contact us today if you’re unsure how to manage cloud connectivity considerations for your product. We can help you assess the pros and cons and make an informed decision for your product development roadmap.