Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) Update
Startups in the Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) industry have a unique opportunity to revolutionize how health care providers and patients access and use medical devices. As part of the digital technology revolution, SaMDs are challenging the conventional definitions and regulatory processes for traditional medical devices.
In this post, we offer a top-level overview of SaMD industry trends, growth, and how SaMD applications are currently making waves in the industry.
What is Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)?
SaMD refers to software applications used to diagnose, treat, monitor, or prevent disease or other medical conditions.
One important distinction to keep in mind is the difference between software used by a connected physical medical device vs. SaMD.
According to the FDA, “Software that is part of a hardware medical device is not SaMD”. The FDA realizes the distinction can be confusing and has provided some examples of what is software for medical devices vs. SaMDs in this document: What are examples of Software as a Medical Device?
SaMD Industry Trends and Growth
The SaMD industry is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advances and changing attitudes toward healthcare. Analysts differ widely in their global growth predictions for the overall sector. For example:
BCC Research projects global SaMD market growth from USD 4.4 B in 2021 to USD 8.2 B in 2027, yielding a CAGR of 11.0%.
Insight Partners reports that the 2019 global SaMD market was USD 18.5 B, and predicts USD 86.5 B in 2027, for an estimated CAGR of 21.9% from 2020 to 2027.
Industry Research.biz estimates the global SaMD market size at USD 1.05 B in 2021 and projects USD 10.2 B by 2028, yielding a CAGR of 38.39%.
Due to the wide variation, SaMD startups may benefit from narrowing their focus on their industry segment when performing market sizing research.
One key trend in the SaMD industry is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatment plans. For example, SaMD applications that use AI and ML can analyze large medical images or patient data datasets to identify patterns and trends that human clinicians might miss.
Related to the AI impact on SaMDs, another industry trend is the growing focus on patient-centric care, with features like personalized treatment plans and remote monitoring capabilities.
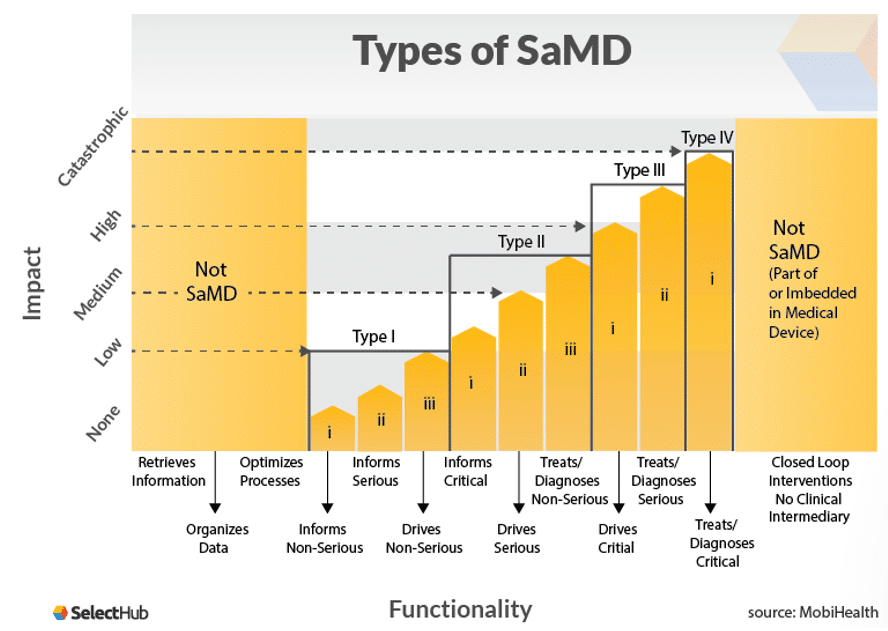
Types of SaMDs
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) has use cases across a wide variety of applications. Here are some examples of SaMD:
- Clinical decision support software: This software provides healthcare professionals with recommendations and guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and management of patient care.
- Medical image analysis software analyzes medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, to help doctors diagnose and treat patients.
- Medical device data system (MDDS) software collects, stores, and transfers data from medical devices, such as heart monitors and blood glucose meters, to electronic health record systems.
- Mobile medical apps: These are applications designed to perform specific medical functions, such as tracking symptoms, monitoring blood pressure, or providing reminders for medication.
- Clinical communication and collaboration software enable healthcare providers to communicate and collaborate, share patient information and clinical data, and coordinate care.
- Health monitoring software monitors and tracks patient health metrics, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, and alerts healthcare providers if any abnormal changes occur.
How the FDA Views SaMDs
Like traditional medical devices, the FDA categorizes SaMD based on the potential risk to patients: Class I, II, and III.
Source: ProRelix Research
The level of risk determines the regulatory pathway the SaMD product must follow for approval.
- Class I: SaMD products considered low-risk under Class I are exempt from premarket submission requirements but must follow general controls and post-market requirements.
- Class II: SaMD products that are moderate-risk under Class II require a premarket submission to demonstrate safety and effectiveness and may also require post-market surveillance.
- Class III: SaMD products that are high-risk under Class III require the most rigorous premarket review and ongoing monitoring and may also need clinical trials to demonstrate safety and effectiveness.
SaMD products are software-based and can be updated frequently over their lifecycle in the marketplace, potentially impacting their safety and effectiveness after approval. That means it is difficult to grant FDA approval for a “final” version. The FDA is working to adapt its approval process to the unique nature of SaMDs.
Currently, the FDA approval process for SaMD products requires careful attention to the level of risk, documentation of software development processes, and ongoing monitoring and reporting of any adverse events or product updates.
FDA SaMD Pre-Certification Pilot
From 2017 to 2022, The FDA supervised a Digital Health Pre-Certification (Pre-Cert) Program for the SaMD pilot to explore ways to streamline the regulatory process for certain types of digital health technologies.
This pilot program aimed to explore a more efficient and patient-centered approach to regulating SaMD by focusing on a software developer’s culture of quality and organizational excellence rather than solely on the product itself.
Companies participating in the FDA Pre-Certification Program include Apple, Fitbit, Johnson & Johnson, Samsung, and Verily (a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc.).
In September 2022, The FDA released its final report along with the decision that a pre-certification working model was impractical to implement under current statutory and regulatory authorities. As of today, there are no planned next steps toward a pre-certification framework.
Succeeding with SaMDs
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is a rapidly growing field that offers many new opportunities for startups to innovate and significantly impact the healthcare industry. However, success in this space requires a deep understanding of the regulatory landscape and a strong focus on ensuring that the technology is effective, reliable, and user-friendly.
SaMD startups that prioritize rigorous testing and validation, user-centered design, and ongoing monitoring and maintenance of their products will be well-positioned to succeed in this exciting and dynamic space.
At Galen Data, we were early movers in the SaMD space, developing a unique, secure cloud-based modular platform for research, reporting, and compliance. Our approach and rolling cost structure allow SaMDs to get up and running in weeks, not months.
Ready for a conversation? Reach out to our CEO Chris DuPont today at 888-372-9175 to discuss your SaMD.






